The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is relatively new to science, but it has always been there. It influences many biological systems in the body, and it can be altered with cannabis use. When we smoke weed, we might never think about how its properties affect us on a molecular level. But it’s a good thing to understand the basics, especially when you’re looking for a specific type of feeling from a specific type of product.
Many physical and mental processes are partially regulated by the ECS, including homeostasis (the balance of our internal systems), appetite, memory, and emotional behaviors. (1) Scientists have also spent decades investigating THC, CBD, and other cannabinoids and their effects on the ECS. They have done so because cannabis isn’t just used recreationally. Study of the therapeutic uses of the cannabis plant is ongoing and is already showing promise in a number of therapeutic settings.
Find the most potent flower, and a host of pre-rolls, edibles, tinctures, and more at Canna Culture. Order for pickup or delivery San Jose, Los Gatos, Mountain View, Cupertino, and beyond. Browse our extensive menu here. Follow the on-screen instructions at checkout to complete your order. If you have questions, just call us directly at (408) 264-7877 or submit a message form on our website.
Contents
The Discovery of the Endocannabinoid System
The ECS was discovered by scientists Allyn Howlett and W.A. Devane in 1988 (1) – a discovery that came much later than the other systems of the human body. For context, the endocrine system was discovered in the 1800s, and the nervous system was even being investigated by the Ancient Greeks! Despite being late to the party, modern-day researchers have been studying the ECS ever since.
The endocannabinoid system is the mechanism through which cannabis takes effect on our bodies. Its components include.
- Fatty acids (lipids), chemical messengers (neurotransmitters), and compounds derived from acids (esters)
- Enzymes that degrade cannabinoids (e.g. hydrolase)
- Cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 in the nervous system
Cannabinoid Discoveries Over the Years
Cannabinoids are important components of the ECS. Each has its own unique properties, despite the fact that we usually only hear about THC and CBD. To date, as well as the “top two”, over 150 minor cannabinoids have been identified by researchers. Cannabinoids isolated from cannabis sativa include the following, and the year in which they were discovered: (2)
- CBD/cannabidiol (1942)
- THC/tetrahydrocannabinol (1964)
- Delta-8-THC/tetrahydrocannabinol (1966)
- CBG/cannabigerol (1972)
- CBN/cannabinol (1972)
- Delta-9-THCa/delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (1975)

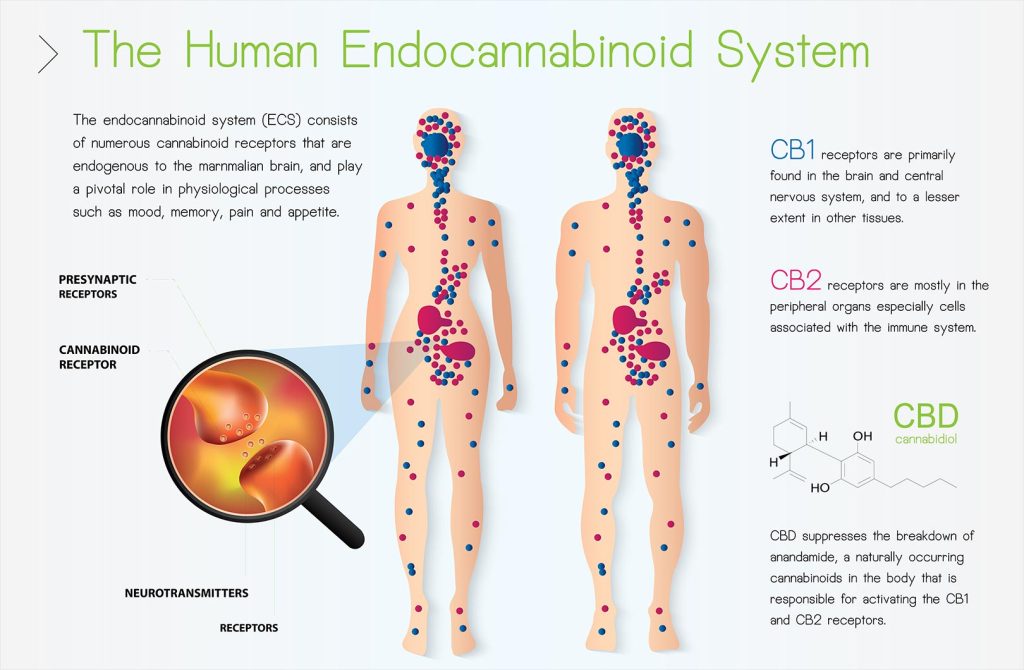
Components of the ECS
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are chemical compounds. There are two distinct classifications. Phytocannabinoids are derived from the cannabis plant. Some well-known cannabinoids include tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD), cannabigerol (CBG), and cannabinol (CBN). Endocannabinoids, as the name suggests, occur naturally in the body. They include specific lipids (fats), the neurotransmitter anandamide (ANA), and 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). (1)
Cannabinoid Receptors
There are two cannabinoid receptor types in the body. They are usually found in cell membranes and work in slightly different ways. (3)
CB1: CB1 receptors are found in numerous places in the brain, including.
- Hippocampus (learning, memory)
- Basal Ganglia (motor control, executive function)
- Cortex (problem-solving, sensorimotor functions)
- Cerebellum (coordinated body movement)
CB2: CB2 receptors are more likely to be found in the peripheral nervous system and elsewhere in the body, such as macrophages (immune cells), tonsils, and spleen.
What Does the ECS Do?
The ECS has many functions, but the two below are the most important.(1)
- Maintaining homeostasis (temperature, mood, and immune system)
- Facilitating energy input and output throughout the body
It also has a strong influence in the following areas.(1)
- Anxiety
- Appetite
- Emotional Behavior
- Depression, Nervous Functions
- Neuron Creation
- Protecting Neurons
- Reward
- Cognition
- Learning
- Memory
- Pain Sensation,
- Fertility, Pregnancy
- Prenatal Development
- Postnatal Development
How Does the ECS Work When I Use Cannabis?
Although the science is a little complex, it’s helpful to think of the ECS as a system that is constantly sending chemical messages around the body. To relate how the ECS works to a metaphor, we can liken the endocannabinoid system to a freeway, CB1 and CB2 receptors as parking spots, our natural endocannabinoids to cars, and cannabis phytocannabinoids to trucks. On a regular day without weed, the cars drive along the freeway, and park in specific spots. But, the parking spots can definitely fit a truck too! In this way, the cannabinoids from cannabis are able to infiltrate our endocannabinoid system, and we are able to get happily blazed!
Therapeutic Properties of CBD
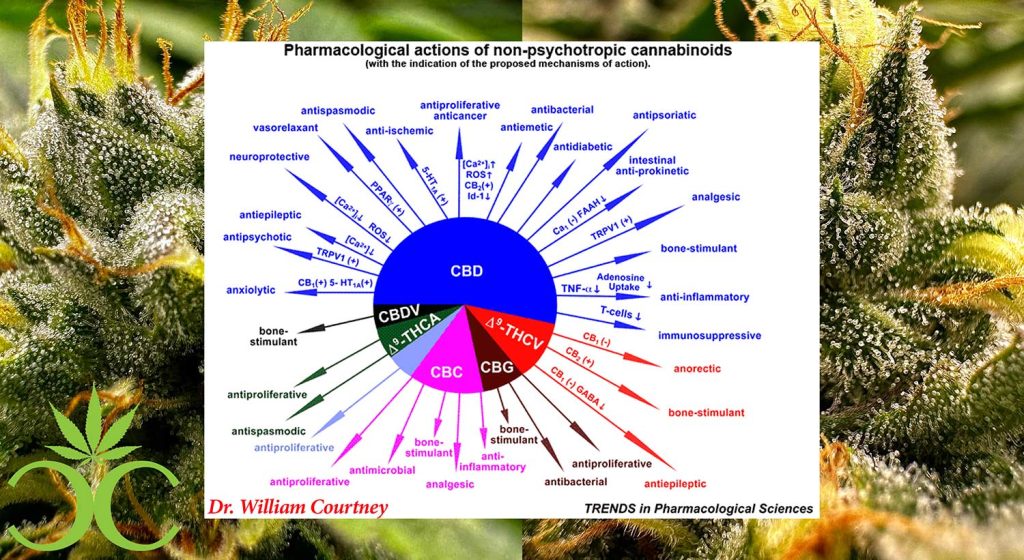
While THC is known to be the major psychoactive agent in cannabis, CBD is a major nonpsychotropic cannabinoid with strong anti-inflammatory, antioxidant properties. (4)
In recent years, scientists have used these substances to help patients with the following physical and mental health conditions. (1)
- Mood Disorders
- Pain Management
- Inflammation
- Diabetes
- Stroke
- Cancer
- Epilepsy
- Schizophrenia
- Autoimmune Conditions
- Skin Conditions
- Eating Disorders
- HIV/AIDS
Shop our delicious CBD-heavy edibles here. And, don’t forget to check out our restorative 3:1. multipurpose salve!
Why Do We Feel Good?
It doesn’t take a seasoned weed connoisseur to know that the effects of cannabis are highly sought-after. The key to its success as humanity’s longest-known medicinal plant is simple – the cannabinoids in weed are almost identical in structure to the endocannabinoids in our body. Smoking for medical reasons or for pleasure, we get the benefits of cannabis because of complex chemical interactions in our bodies!
THC mimics the chemical structure of the endocannabinoid anandamide. Because it’s so similar in structure, the brain can’t tell the difference, which allows THC to alter our brain’s communication with the rest of the body. THC attaches to CB1 receptors, disrupting the chemical messages that involve pleasure, memory, concentration, coordination, and more. (5)
Buy NowCanna Culture VIP Rewards
Become a VIP and take advantage of the best deals at Canna Culture without VIP rewards program!
Member Perks:
- Get 2% back for every dollar you spend (before tax)
- Bring your friends and family and get a pre-roll for under $2
- Get notified first about our demo days with bogo
Sign yourself up for our VIP Rewards Program and get what you want at a great price. Get the lowdown on what our loyal clients love about Canna Culture products by reading our glowing reviews.
Quality Cannabis at Canna Culture
Harness the power of your own ECS by shopping our full menu of high THC products.
High THC Selection
High CBD Selection
Lesser-Known Cannabinoid Selection
- CannaBiotics Endocannabinoid Nutritional Supplement 30 Capsules (THCa 2mg, CBDa 1mg, 50 Total Cannabinoids per Capsule)
- Purple Trainwreck Flower (25% THC – 4.3% Terpenes)
- CKC Extract Badder (80% THCa )
- Heavy Hitters Lights On 2:1 THCV Gummies (50mg THCV – 100mg THC )
- Wyld 2:1 CBN Sleep Gummies (50mg CBN – 100mg THC )
- Level Protab+ Lights Out Sleep Tablets (200mg ∆9 THC – 50mg CBN – 50mg ∆8 THC – 20mg THCa – 20mg CBG )
Weed for Delivery in San Jose, CA
Get the most out of your purchase with Canna Culture, San Jose and Silicon Valley’s premier cannabis dispensary! Order online for pickup or delivery and find out what our products can do for your endocannabinoid system. Our budtenders are ready and willing to take your call, so if you have any questions before you buy, call us at (408) 264-7877. You can also contact us online by filling out a quick form with your query.
Join Canna Culture on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter for our weekly specials, and the latest events in the San Jose area. And don’t forget to read about Canna Culture News on our blog!
References
- Lowe H, Toyang N, Steele B, Bryant J, Ngwa W. The Endocannabinoid System: A Potential Target for the Treatment of Various Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021;22(17):9472. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179472
- Shahbazi F, Grandi V, Banerjee A, Trant JF. Cannabinoids and Cannabinoid Receptors: The Story so Far. iScience. 2020;23(7):101301. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2020.101301
- Howlett AC, Abood ME. CB 1 and CB 2 Receptor Pharmacology. Cannabinoid Pharmacology. Published online 2017:169-206. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.apha.2017.03.007
- Alger BE. Getting high on the endocannabinoid system. Cerebrum : the Dana forum on brain science. 2013;2013:14. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3997295/
- National Institute on Drug Abuse. How does marijuana produce its effects? National Institute on Drug Abuse. Published July 2020. https://nida.nih.gov/publications/research-reports/marijuana/how-does-marijuana-produce-its-effects